The Basics of a Mechanical Fuel Pump
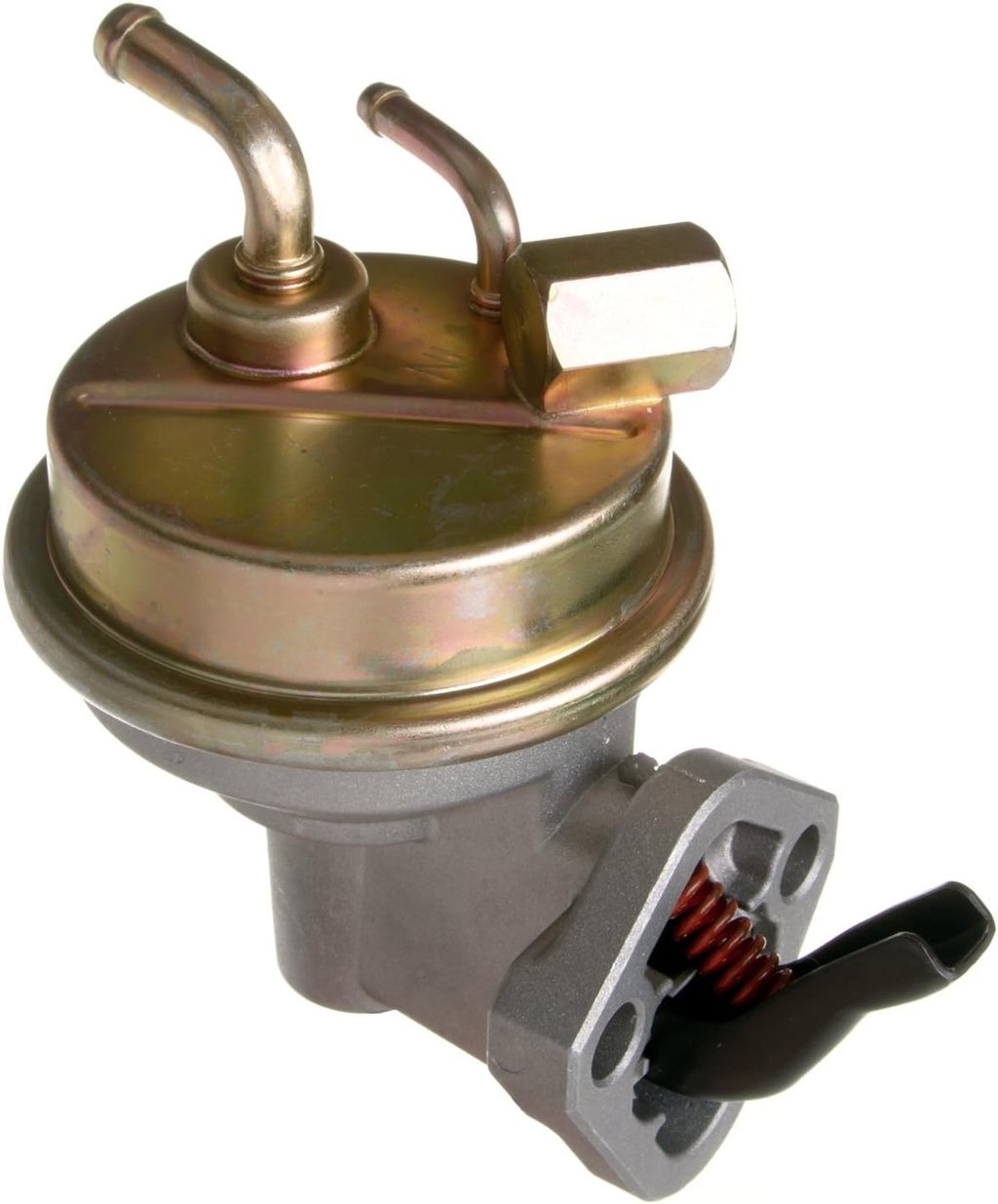
A mechanical fuel pump is a crucial component of a vehicle's fuel system, responsible for delivering fuel from the gas tank to the engine. Unlike its electric counterpart, a mechanical fuel pump relies on the motion of the engine to function. In this article, we will explore the inner workings of a mechanical fuel pump and how it ensures a steady supply of fuel to keep your vehicle running smoothly.
The Function of a Mechanical Fuel Pump
A mechanical fuel pump's primary function is to draw fuel from the gas tank and deliver it to the carburetor or fuel injection system of the engine. It achieves this through a series of mechanical processes that work in harmony to create the necessary pressure for fuel delivery.
Fuel Pump Diaphragm
One of the key components of a mechanical fuel pump is the diaphragm. This flexible rubber membrane is responsible for creating the pumping action. As the engine rotates, a lever connected to the camshaft moves up and down, causing the diaphragm to reciprocate. When the diaphragm moves downward, it creates a vacuum that draws fuel into the pump from the gas tank.
Inlet and Outlet Valves
The mechanical fuel pump also features inlet and outlet valves that control the flow of fuel. When the diaphragm moves upward, it compresses the fuel in the pump chamber, forcing it out through the outlet valve. Conversely, when the diaphragm moves downward, the inlet valve opens, allowing fuel to enter the pump chamber.
Advantages of a Mechanical Fuel Pump
Mechanical fuel pumps offer several advantages over their electric counterparts. Firstly, they are generally more reliable since they do not rely on electrical components that can fail. Secondly, they provide a consistent fuel supply, ensuring that the engine receives the required amount of fuel at all times. Additionally, mechanical fuel pumps are often more affordable and easier to maintain compared to electric fuel pumps.
Common Issues and Troubleshooting
While mechanical fuel pumps are generally reliable, they can still experience issues over time. Two common problems include fuel leaks and pump failure. If you notice a strong smell of gasoline or puddles of fuel under your vehicle, it may indicate a fuel pump leak. In such cases, it is important to have the issue addressed promptly to prevent any safety hazards.
If your vehicle experiences sudden fuel delivery issues or struggles to start, it could be a sign of a failing mechanical fuel pump. In such instances, it is advisable to consult a professional mechanic who can diagnose and repair the problem.
Conclusion
In conclusion, a mechanical fuel pump plays a vital role in delivering fuel from the gas tank to the engine. Through the movement of a diaphragm, the pump creates pressure that forces fuel to flow to the carburetor or fuel injection system. Understanding how a mechanical fuel pump works can help you identify and address any potential issues, ensuring the smooth operation of your vehicle's fuel system.