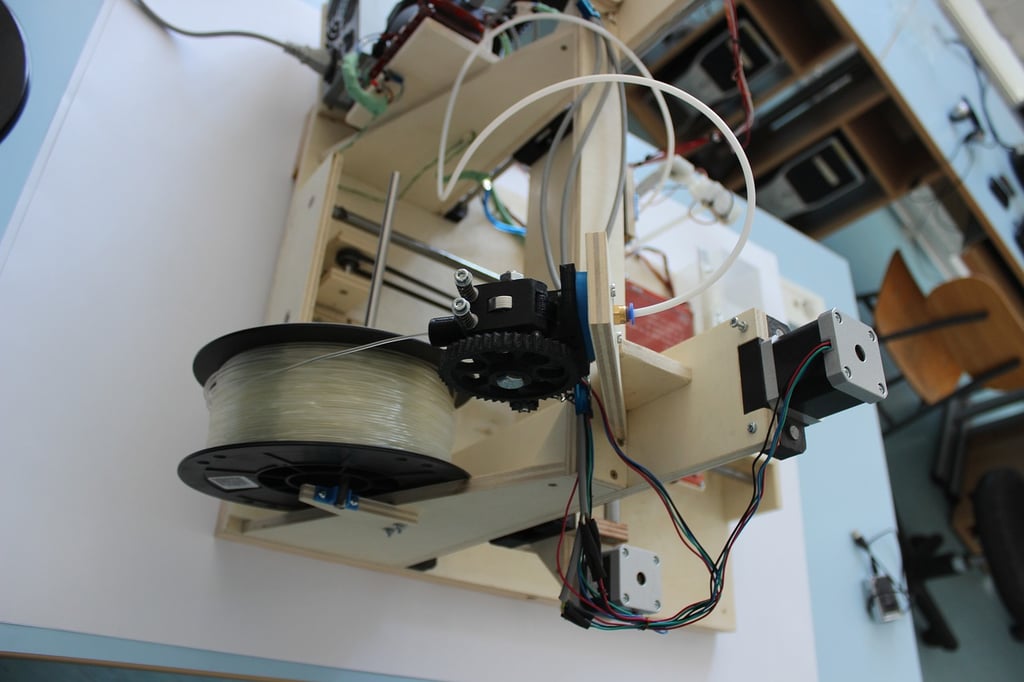
Understanding the Complexity of 3D Printing
3D printing has revolutionized various industries, allowing individuals and businesses to create intricate designs and functional prototypes with ease. However, for those who are new to the world of additive manufacturing, the question often arises: is 3D printing hard? In this article, we will explore the different aspects of 3D printing to provide you with a comprehensive understanding of its complexity.

The Basics of 3D Printing
Before delving into the intricacies of 3D printing, it is essential to grasp the fundamentals of this technology. At its core, 3D printing is a process that transforms digital designs into physical objects by layering materials on top of each other. This is achieved through a specialized machine known as a 3D printer.
3D printers utilize various technologies, such as fused deposition modeling (FDM) or stereolithography (SLA), to bring digital designs to life. FDM printers extrude melted filament onto a build plate, while SLA printers use a laser to solidify liquid resin layer by layer. Both methods have their advantages and complexities, but for beginners, FDM printers are often recommended due to their affordability and user-friendly nature.
Choosing the Right 3D Printer
When it comes to 3D printing, selecting the right printer is crucial. While there is a wide range of options available on the market, each with its own set of features and capabilities, beginners should prioritize ease of use and reliability.
Entry-level 3D printers, such as the Creality Ender 3 or Prusa i3 MK3, are popular choices for beginners. These printers offer a balance between affordability and functionality, making them ideal for those who are just starting their 3D printing journey. Additionally, these models often have a supportive online community, providing valuable resources and troubleshooting tips.

Learning the Software
One of the key challenges beginners face when diving into 3D printing is learning the software required to design and prepare 3D models for printing. While it may seem daunting at first, there are user-friendly software options available that simplify the process.
Software like Tinkercad and Fusion 360, both developed by Autodesk, are excellent choices for beginners. These programs offer intuitive interfaces and a wide range of tutorials to help you get started. Additionally, there are numerous online communities and forums where you can seek guidance and learn from experienced users.
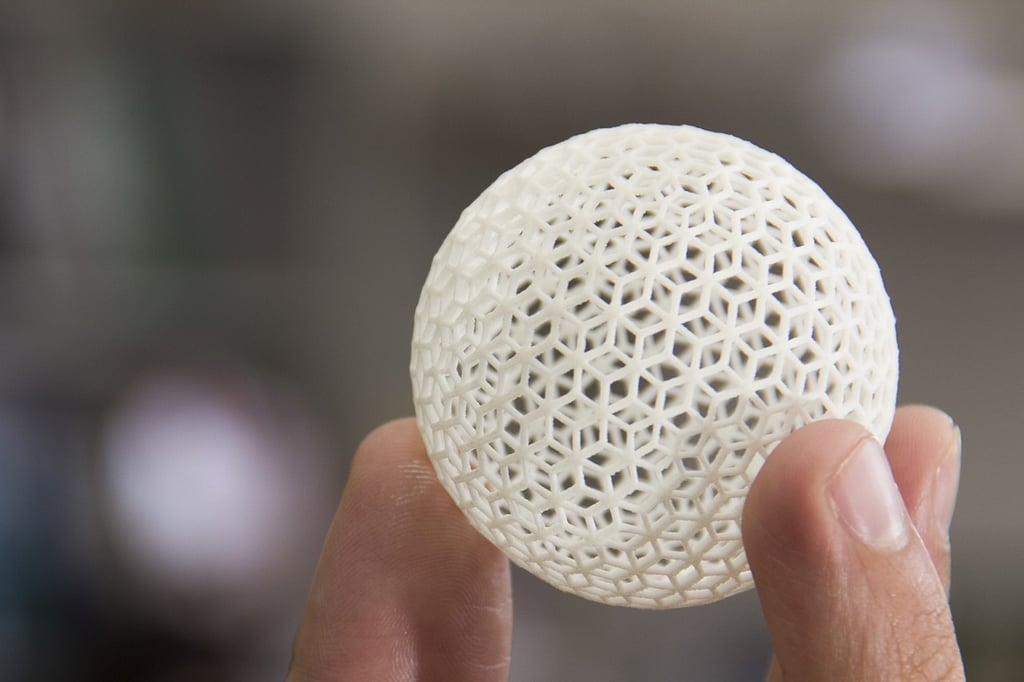
Understanding the Importance of Calibration
Calibration plays a vital role in achieving successful 3D prints. It involves adjusting various settings, such as bed leveling, nozzle height, and extrusion flow, to ensure precise and accurate prints. While calibration can be time-consuming, it is a necessary step to achieve optimal results.
Fortunately, most 3D printers come with built-in calibration routines, making the process more accessible for beginners. Additionally, online resources and guides provide step-by-step instructions on how to calibrate your specific printer model.
Mastering Troubleshooting Techniques
As with any technology, 3D printing can sometimes present challenges. From failed prints to clogged nozzles, troubleshooting is an essential skill for any 3D printing enthusiast.
By familiarizing yourself with common issues and their solutions, you can save time and frustration. Online communities, such as Reddit's r/3Dprinting or dedicated forums like 3D Printing Stack Exchange, are excellent platforms to seek advice and learn from experienced users.
Here are a few steps for printing with a 3D printer:
Design or download a 3D model:
The first step is to have a 3D model of the object you want to print. You can either design it yourself using 3D modeling software or download ready-made models from various online platforms.
Prepare the model for printing:
Once you have the 3D model, you need to prepare it for printing. This involves using slicing software that takes the 3D model and converts it into a set of instructions that the 3D printer can understand. In this step, you can adjust settings like layer height, infill density, and support structures.
Load filament:
Next, load the appropriate filament into your 3D printer. Filament is the material used for printing, such as PLA, ABS, or PETG. Follow the instructions of your specific printer to load the filament correctly.
Calibrate the printer:
Before starting the print, it's crucial to calibrate the 3D printer. This involves ensuring that the print bed is leveled and the nozzle height is correctly set. Proper calibration helps in achieving accurate prints.
Start the print:
Once everything is set up, start the print from the slicing software. The printer will heat the nozzle and the print bed to the required temperature. It will then begin printing the object layer by layer, following the instructions generated by the slicing software.
Monitor the print:
While the printer is working, it's essential to keep an eye on the progress. Check if the layers are adhering properly and if any issues arise during the print. This way, you can address any problems that may occur in real-time.
Post-processing:
After the print is completed, you might need to perform some post-processing steps depending on the desired outcome. This can include removing support structures, sanding rough surfaces, or applying finishing touches like painting or polishing.
These steps provide a general overview of the process, but it's important to note that the specific steps and procedures may vary depending on the type and model of the 3D printer you are using. Always refer to the manufacturer's instructions for your specific printer model.

The following are common questions and solutions about 3D printing:
Printing Quality: Achieving high-quality prints can be challenging due to issues like layer lines, surface roughness, or inconsistencies.
To overcome this, you can:
- Adjust the print settings like layer height, print speed, and temperature to optimize the print quality.
- Use high-quality filaments and ensure proper calibration of the printer.
- Implement post-processing techniques like sanding, polishing, or painting to enhance the final print's appearance.
Print Warping: Certain materials, such as ABS, can experience warping or lifting from the build plate during printing.
This can lead to failed prints or distorted shapes. You can address this by:
- Ensuring a heated print bed and using adhesives like glue stick, hairspray, or specialized bed adhesives to improve adhesion.
- Adding a brim or raft around the print to increase the surface area and minimize warping.
- Enclosing the printer in a chamber to maintain a stable temperature throughout the printing process.
Support Structures: Complex or overhanging designs may require support structures to prevent sagging or collapsing during printing. Removing these supports can be time-consuming and may leave marks on the final print.
To tackle this:
- Design models with self-supporting angles wherever possible, minimizing the need for additional supports.
- Utilize soluble support materials that can be dissolved using specific solvents, reducing the effort required for support removal.
- Experiment with different support settings in slicing software to optimize the balance between support strength and ease of removal.
Print Speed: 3D printing can be a slow process, especially for large or highly detailed prints.
While print speed depends on various factors like layer height and complexity, you can try:
- Adjusting the print speed settings in the slicer software, finding the optimal balance between speed and print quality.
- Utilizing larger nozzle sizes to increase print speed without compromising too much on quality.
- Considering the use of multiple printers simultaneously for faster production, especially for high-demand scenarios.
Material Limitations: Different materials have specific requirements and limitations in the 3D printing process.
To overcome material-related challenges:
- Research and understand the properties and characteristics of the chosen filament or resin before printing.
- Optimize print settings, such as temperature, speed, and cooling, for the specific material being used.
- Explore alternative materials or filaments that may better suit your desired outcome or application.
Overall, overcoming these difficulties often involves a combination of experimentation, calibration, software optimization, and material knowledge to achieve the desired 3D printing results.
Relative Articles
-
What is an Extruder in 3D Printing?
-
How to Remove Raft from 3D Print: A Step-by-Step Guide
-
How to Clean Up Stringing on 3D Print
-
How to Calibrate Your 3D Printer for Optimal Performance
-
Can I Pause a 3D Print Overnight? Exploring the Pros and Cons

-
How to 3D Print Large Objects
-
How to Recycle 3D Printer Filament: A Comprehensive Guide

-
How to Make 3D Printer Filament from Plastic Bottles