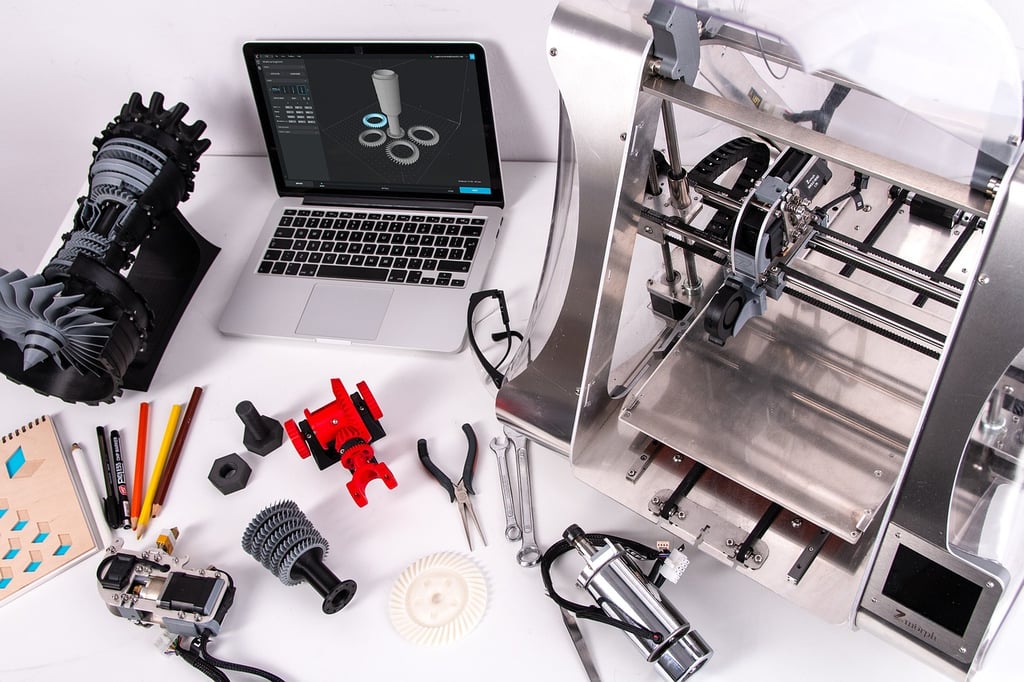
The Role of an Extruder in 3D Printing
3D printing technology has revolutionized various industries, allowing for the creation of complex and customized objects with ease. One of the key components that make 3D printing possible is the extruder. In this article, we will explore what an extruder is in the context of 3D printing and its role in the additive manufacturing process.
Understanding the Basics: What is an Extruder?
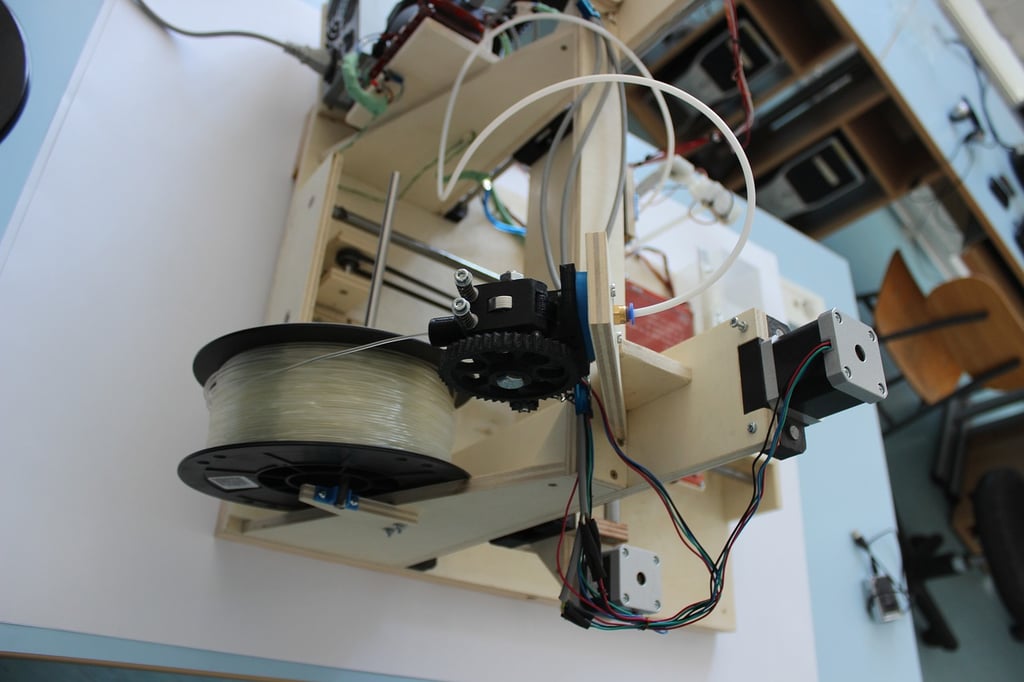
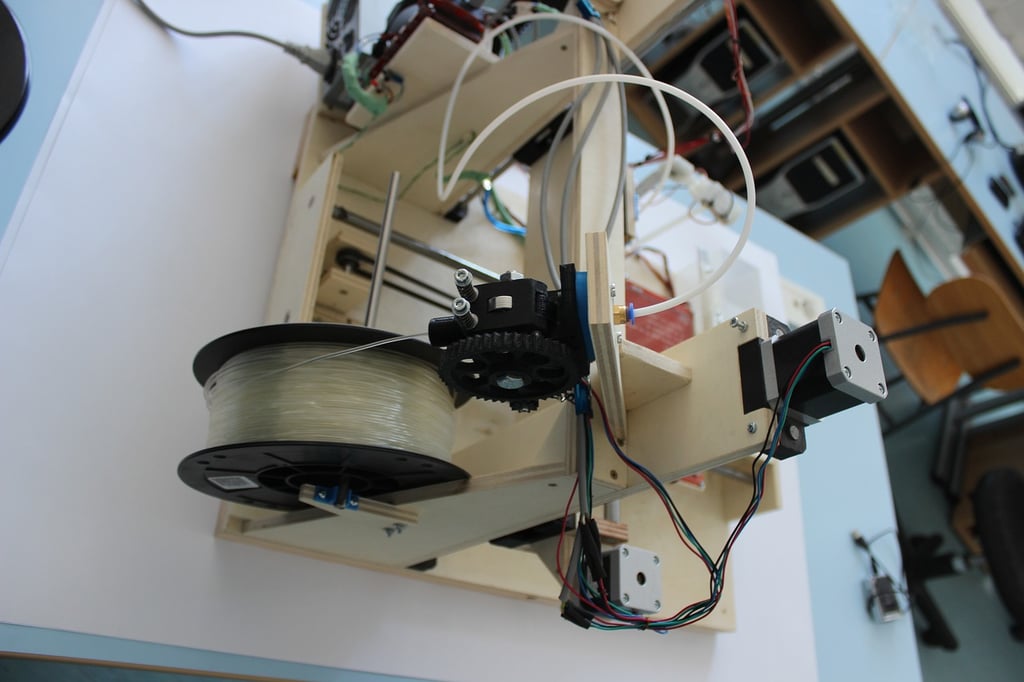
At its core, an extruder is a device that transforms raw material, typically in the form of filament, into a molten state and then deposits it layer by layer to create a three-dimensional object. In the context of 3D printing, the extruder is responsible for heating and melting the filament and accurately depositing it according to the design specifications.
The Components of an Extruder
An extruder consists of several essential components that work in harmony to ensure a smooth and precise 3D printing process. These components include:
1. Nozzle
The nozzle is the part of the extruder that controls the flow of the molten filament. It has a small opening through which the filament is pushed, allowing for precise deposition of the material layer by layer. Nozzles come in different sizes, which affects the resolution and speed of the printing process.
2. Heat Block
The heat block is responsible for heating the filament to its melting point. It contains a heating element, such as a resistor, that raises the temperature of the block and consequently melts the filament. The temperature is carefully controlled to ensure proper melting without causing any damage to the filament or the printer.
3. Heater Cartridge
The heater cartridge is a small electric heater that is inserted into the heat block. It provides the necessary heat to melt the filament and maintain a consistent temperature throughout the printing process. The power of the heater cartridge determines how quickly the filament can be melted and extruded.
4. Cooling Fan
A cooling fan is often included in the extruder design to rapidly cool down the freshly deposited filament. This is essential to ensure that each layer solidifies quickly and maintains its shape. The cooling fan helps in preventing warping or distortion of the printed object.
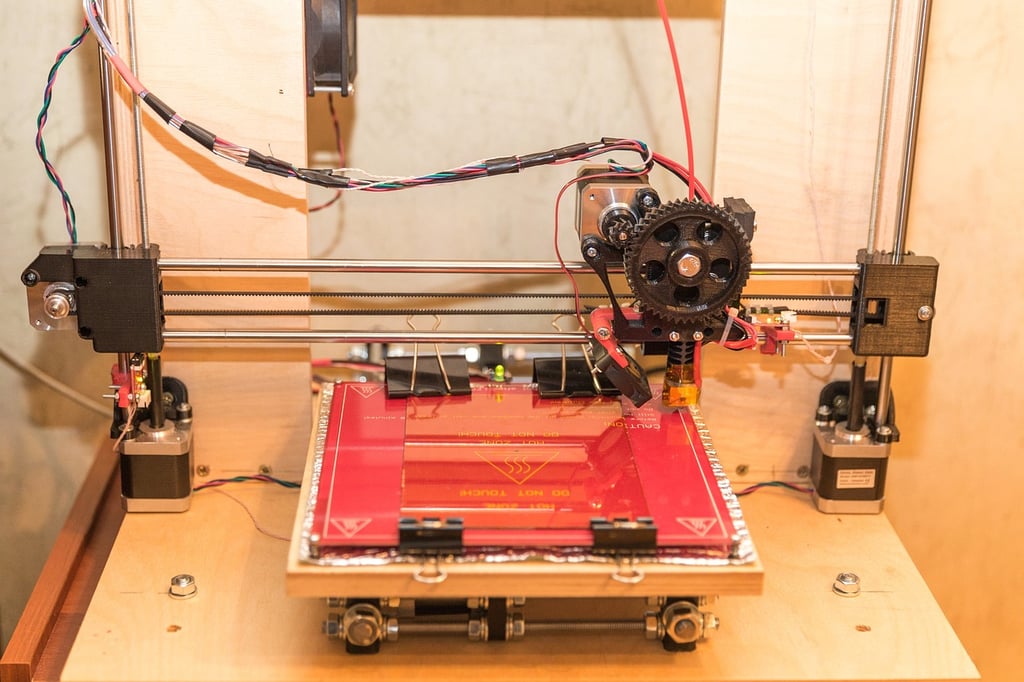
The Extrusion Process
Now that we understand the components of an extruder, let's take a closer look at the extrusion process in 3D printing:
1. Filament Loading
The first step in the extrusion process is loading the filament into the extruder. The filament is typically made of thermoplastic materials such as ABS or PLA. It is fed into the extruder through a tube and guided towards the nozzle.
2. Filament Heating and Melting
Once the filament is loaded, the extruder's heater cartridge and heat block work in tandem to raise the temperature and melt the filament. The molten filament is then ready for extrusion through the nozzle.
3. Layer-by-Layer Deposition
As the extruder pushes the molten filament through the nozzle, it is deposited layer by layer onto the print bed or previously printed layers. The extruder moves in a controlled manner, following the design instructions, to create the desired shape and structure.
4. Cooling and Solidification
After each layer is deposited, the cooling fan comes into play. It rapidly cools down the molten filament, allowing it to solidify and maintain its shape. The cooling process is critical in ensuring dimensional accuracy and preventing any deformations.
The Importance of a Well-Calibrated Extruder
Having a well-calibrated extruder is crucial for achieving high-quality 3D prints. Proper calibration ensures that the extruder is accurately pushing the filament and depositing it in the right amounts. An improperly calibrated extruder can lead to under-extrusion or over-extrusion, resulting in issues such as weak prints, poor layer adhesion, or clogged nozzles.
Regular maintenance and calibration of the extruder, including checking the nozzle diameter, adjusting the extrusion multiplier, and cleaning any debris, are necessary to ensure consistent and reliable 3D printing results.
Conclusion
An extruder is a fundamental component of any 3D printer, responsible for heating, melting, and depositing filament to create three-dimensional objects. Understanding its role and the various components involved in the extrusion process is essential for achieving high-quality prints. By properly calibrating and maintaining the extruder, users can unlock the full potential of 3D printing technology and explore its endless possibilities.
Relative Articles
-
Is 3D Printing Hard? Exploring the Prospects of This Innovative Technology

-
How to Remove Raft from 3D Print: A Step-by-Step Guide
-
How to Clean Up Stringing on 3D Print
-
How to Calibrate Your 3D Printer for Optimal Performance
-
Can I Pause a 3D Print Overnight? Exploring the Pros and Cons

-
How to 3D Print Large Objects
-
How to Recycle 3D Printer Filament: A Comprehensive Guide

-
How to Make 3D Printer Filament from Plastic Bottles